Tracing using the Arize SDK
Langfuse offers an OpenTelemetry backend to ingest trace data from your LLM applications. With the Arize SDK and OpenTelemetry, you can log traces from multiple other frameworks to Langfuse. Below is an example of tracing OpenAI to Langfuse, you can find a full list of supported frameworks here. To make this example work with other frameworks, you just need to change the instrumentor to match the framework.
Arize AI SDK: Arize AI provides Openinference, a library that is complimentary to OpenTelemetry to enable tracing of AI applications. OpenInference can be used with any OpenTelemetry-compatible backend.
Step 1: Install Dependencies
Install the necessary Python packages to enable OpenTelemetry tracing, openinference instrumentation, and the OpenAI SDK for making LLM requests.
%pip install arize-phoenix-otel openai openinference-instrumentation-openaiStep 2: Configure Environment Variables
Set your Langfuse API keys for the basic auth header. Get your Langfuse API keys by signing up for Langfuse Cloud or self-hosting Langfuse.
Also, add your OPENAI_API_KEY as an environment variable.
import os
import base64
LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY = "pk-lf-..."
LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY = "sk-lf-..."
LANGFUSE_AUTH = base64.b64encode(f"{LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY}:{LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY}".encode()).decode()
os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com/api/public/otel" # 🇪🇺 EU data region
# os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com/api/public/otel" # 🇺🇸 US data region
os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS"] = f"Authorization=Basic {LANGFUSE_AUTH}"
# Set your OpenAI API key.
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-proj-..."Configure tracer_provider and add a span processor to export traces to Langfuse. OTLPSpanExporter() uses the endpoint and headers from the environment variables.
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace import TracerProvider
from opentelemetry.exporter.otlp.proto.http.trace_exporter import OTLPSpanExporter
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace.export import SimpleSpanProcessor
trace_provider = TracerProvider()
trace_provider.add_span_processor(SimpleSpanProcessor(OTLPSpanExporter()))
# Sets the global default tracer provider
from opentelemetry import trace
trace.set_tracer_provider(trace_provider)
# Creates a tracer from the global tracer provider
tracer = trace.get_tracer(__name__)Step 3: Initialize Instrumentation
Initialize the Arize Phoenix module register(). By setting set_global_tracer_provider = False, we can use the OpenTelemetry tracer provider we created in the previous step. Then, we can use the OpenAIInstrumentor to instrument the OpenAI SDK. You can replace this with any of the frameworks supported here
# from phoenix.otel import register
from phoenix.otel import register
from openinference.instrumentation.openai import OpenAIInstrumentor
# configure the Phoenix tracer
register(set_global_tracer_provider = False,)
OpenAIInstrumentor().instrument()🔭 OpenTelemetry Tracing Details 🔭
| Phoenix Project: default
| Span Processor: SimpleSpanProcessor
| Collector Endpoint: localhost:4317
| Transport: gRPC
| Transport Headers: {'authorization': '****', 'user-agent': '****'}
|
| Using a default SpanProcessor. `add_span_processor` will overwrite this default.Step 4: Execute a Sample LLM Request
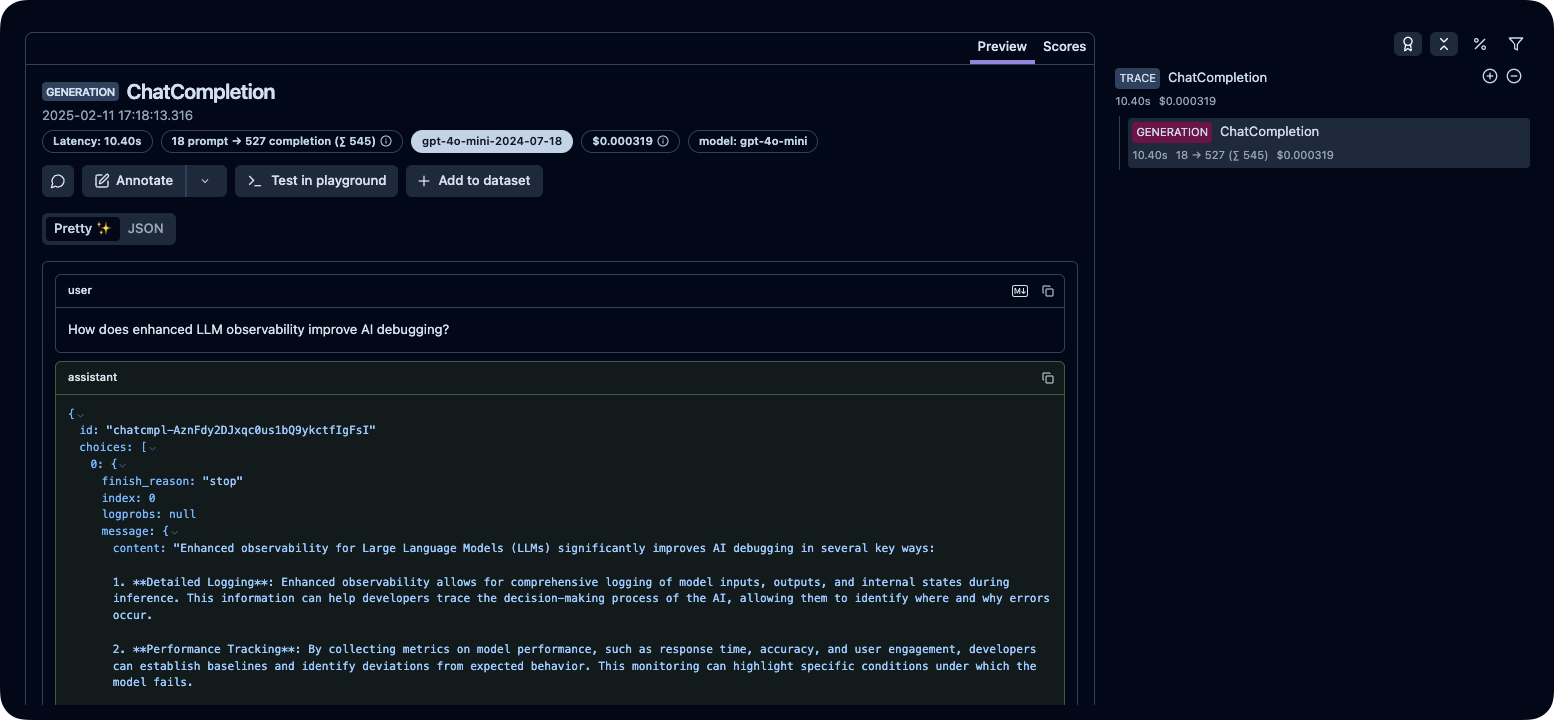
With instrumentation enabled, every OpenAI API call will now be traced. The following example sends a chat completion request to illustrate the integration.
import openai
response = openai.OpenAI().chat.completions.create(
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "How does enhanced LLM observability improve AI debugging?",
}
],
model="gpt-4o-mini",
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)Step 5: Pass Additional Attributes (Optional)
Opentelemetry lets you attach a set of attributes to all spans by setting set_attribute. This allows you to set properties like a Langfuse Session ID, to group traces into Langfuse Sessions or a User ID, to assign traces to a specific user. You can find a list of all supported attributes in the here.
import openai
with tracer.start_as_current_span("OpenAI-Trace") as span:
span.set_attribute("langfuse.user.id", "user-123")
span.set_attribute("langfuse.session.id", "123456789")
span.set_attribute("langfuse.tags", ["staging", "demo"])
span.set_attribute("langfuse.prompt.name", "test-1")
# You application code below:
response = openai.OpenAI().chat.completions.create(
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "How does enhanced LLM observability improve AI debugging?",
}
],
model="gpt-4o-mini",
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)Step 6: View the Traces in Langfuse
After running the above code, you can inspect the generated traces on your Langfuse dashboard: